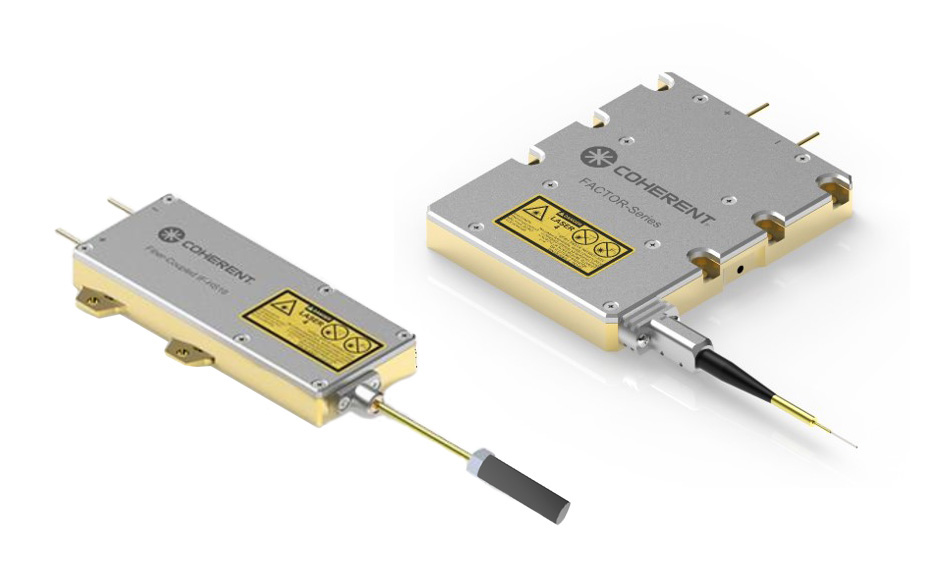
In the world of photonics, multimode laser diodes have carved a significant niche, blending efficiency with versatility. These devices, recognized for their robust optical power output and ability to support multiple transverse modes, are indispensable in a myriad of applications, from telecommunications to medical instrumentation.
What Are Multimode Laser Diodes?
At their core, multimode laser diodes are semiconductor-based light sources designed to emit laser beams with multiple spatial modes. Unlike single-mode diodes that produce a highly focused beam, these lasers generate broader and more divergent outputs. This characteristic stems from their cavity design, allowing multiple transverse electromagnetic waves to resonate simultaneously.
The result? A higher power output and a broader emission profile. These properties make them ideal for applications where precision isn’t the sole priority, but power and adaptability are critical.
Key Characteristics of Multimode Laser Diodes
- Higher Power Outputs: The capacity to support multiple modes allows multimode laser diodes to emit significantly more power compared to their single-mode counterparts. This makes them especially suitable for tasks such as material processing and pumping solid-state lasers.
- Beam Divergence: While the divergence of the beam might limit certain high-precision applications, it proves advantageous in areas like illumination or spectroscopy, where a wider beam spread is beneficial.
- Wavelength Range: These diodes are available across a diverse range of wavelengths, from visible to near-infrared, offering flexibility to cater to varied industry needs.
Applications Across Industries
Multimode laser diodes shine brightest when utilized in scenarios that demand both power and efficiency.
- Telecommunications: While single-mode lasers dominate fiber optics, multimode diodes are invaluable in shorter-range communication systems. They power multimode fiber networks, enabling efficient data transmission over distances where beam quality isn’t a limiting factor.
- Medical Equipment: In medical fields, these lasers are used for applications such as photodynamic therapy and surgical illumination. Their ability to deliver high-power beams ensures effective and precise treatments.
- Industrial Uses: From cutting and welding to engraving, the higher power levels of multimode laser diodes make them indispensable in manufacturing processes. Their broader beam allows for uniform energy distribution over larger surfaces.
- Consumer Electronics: Devices like projectors and barcode scanners leverage these diodes for their compact size and reliable performance.
Advantages of Multimode Laser Diodes
- Cost-Effectiveness: Their design simplicity and ease of manufacturing make them a more affordable choice compared to more complex laser systems.
- Durability and Reliability: These diodes are built to withstand rigorous operating conditions, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.
- Energy Efficiency: By converting electrical energy into light with minimal losses, they contribute to sustainable practices in various industries.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, multimode laser diodes come with challenges. The beam divergence can be a drawback for applications requiring high spatial coherence. Additionally, their broader spectral linewidth might limit their use in scenarios demanding extreme wavelength precision, such as high-resolution spectroscopy.
Heat management is another critical consideration. Higher power outputs generate significant thermal energy, necessitating robust cooling systems to maintain performance and longevity.
The Future of Multimode Laser Diodes
The evolution of multimode laser diodes is driven by advancements in semiconductor materials and fabrication techniques. Researchers are constantly innovating to enhance efficiency, reduce thermal loads, and improve beam quality. Emerging applications, such as autonomous vehicle LiDAR systems and advanced medical diagnostics, promise to expand the scope of these versatile devices.
Moreover, the integration of these diodes with smart systems and artificial intelligence opens new frontiers in adaptive lighting, precision agriculture, and beyond. Their role in shaping a more interconnected and energy-efficient future cannot be overstated.
Conclusion
Multimode laser diodes stand at the intersection of power, efficiency, and versatility. Whether in industrial, medical, or consumer applications, they continue to prove their value across a broad spectrum of uses. As technology advances, these robust light sources will undoubtedly find even more groundbreaking applications, reinforcing their place as a cornerstone in the realm of photonics.