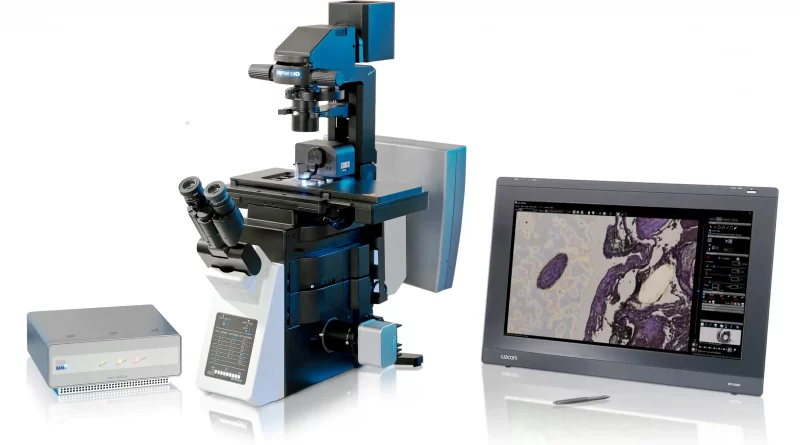
In the world of molecular biology, precision is key. Understanding the complex interactions within tissues and cells is crucial for advancing research in areas like cancer, neuroscience, and genomics. One powerful tool that has revolutionized tissue analysis is laser capture microdissection microscope, a cutting-edge technique that allows researchers to isolate specific cells or tissue regions with high accuracy, paving the way for more targeted and insightful studies.
What is Laser Capture Microdissection (LCM)?
Laser capture microdissection is a technique used to isolate specific cells or regions from a tissue sample using a focused laser beam. This method enables scientists to extract small, defined portions of tissue for further analysis, all while preserving the molecular integrity of the sample. Whether it’s a single cell or a specific region of interest within a larger tissue section, LCM allows researchers to target and capture precise tissue areas without disturbing the surrounding architecture.
The Technology Behind LCM
The process of laser capture microdissection begins with the preparation of tissue samples, often fixed on glass slides. The sample is then visualized under a microscope, where a laser is used to dissect the targeted area. The tissue is then lifted using a special membrane, which can be transferred to a collection device for further molecular analysis. This technique ensures that only the selected tissue is extracted, enabling focused studies on specific cells or cellular components without contamination from neighboring tissues.
What makes this technique so revolutionary is its ability to work with minute tissue samples, down to the single-cell level. This precision allows researchers to gather critical molecular data that might otherwise be missed in bulk tissue analysis.
Applications of LCM in Research
Laser capture microdissection is a versatile tool with wide-ranging applications in various fields of research. Here are a few examples of how LCM is being used to drive scientific discovery:
- Oncology: LCM is particularly useful in cancer research, where scientists can isolate specific tumor cells from the surrounding tissue. This enables the study of the tumor microenvironment, helping researchers identify molecular markers and understand the mechanisms of cancer progression.
- Neuroscience: The human brain is made up of thousands of different cell types, many of which are difficult to study in isolation. LCM allows researchers to capture specific neurons or other cells in the central nervous system, enabling more targeted investigations into neurodegenerative diseases and brain function.
- Genomics and Proteomics: By isolating precise regions of tissue, LCM facilitates the analysis of DNA, RNA, and proteins at a level of detail that was previously unattainable. Researchers can profile the genome or transcriptome of specific cell types within a heterogeneous tissue sample, opening the door to a deeper understanding of gene expression and protein function.
Advantages of LCM in Spatial Biology
One of the primary advantages of LCM is its ability to integrate spatial context into molecular profiling. Traditional molecular techniques often analyze homogenized tissue samples, losing valuable information about where specific molecules or cells reside within the tissue. With LCM, researchers can analyze tissue samples while preserving the spatial arrangement of cells, offering a more comprehensive view of the tissue’s molecular landscape.
Additionally, LCM enables multi-omic profiling, combining genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic data from the same tissue sample. This multi-modal approach provides a more complete understanding of the tissue microenvironment and the biological processes occurring within it.
The Future of Laser Capture Microdissection
As the field of molecular biology continues to evolve, laser capture microdissection is becoming an increasingly vital tool in the research toolkit. Advances in imaging technology and data analysis software are making it easier than ever to capture, analyze, and interpret tissue samples with unprecedented precision.
Moreover, the integration of AI and machine learning is helping to automate and enhance the accuracy of LCM, further accelerating the discovery process. The potential applications of this technology are vast, and we can expect to see even more groundbreaking research in fields such as precision medicine and personalized therapies.
Conclusion
Laser capture microdissection is a powerful technique that is transforming the way scientists study tissues and cells. By offering unparalleled precision and the ability to preserve the molecular integrity of samples, LCM is enabling more targeted and insightful research across various disciplines. As the technology continues to advance, the possibilities for using LCM in scientific discovery are endless.
To learn more about how laser capture microdissection is advancing precision medicine, check out the AccuLift™ LCM laser capture microdissection microscope.